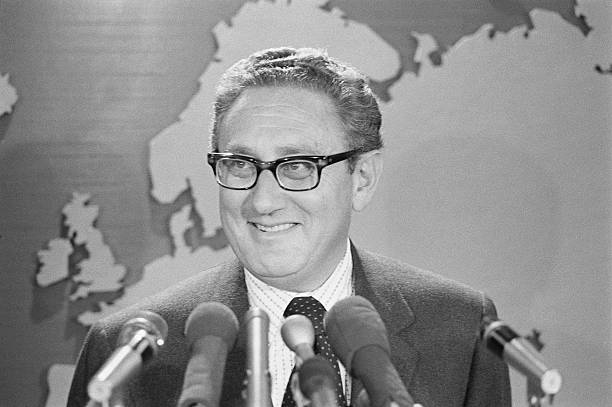
Henry Kissinger, a prominent figure in American politics, passed away on November 29, 2023, leaving many of the younger generation—myself included—to wonder: who exactly was Henry Kissinger and why should we care?
Known for his influential role as a statesman and diplomat, Kissinger was born in Germany, on May 27, 1923. He fled the Nazi regime with his family, eventually settling in the United States. His political career took off during the Cold War era, and he became a key architect of U.S. foreign policy.
For a more generational take I asked my mother, Jodie Ellis, what Henry Kissinger’s legacy was to her:
“I was a bit young when he was in office but I completely respect him as a brilliant statesman/diplomat with a very intelligent and bright mind.”
Another Petaluma Parent, who prefers to remain unnamed, stated that “Kissinger was before my time, I was just a kid when he was in his prime, but as a history major in college I can say that he was a powerhouse of a statesman.”
Kissinger served as National Security Advisor and later the Secretary of State under Presidents Richard Nixon and Gerald Ford. One of his notable achievements was his role in negotiating the Paris Peace Accords in 1973, which helped end the Vietnam War. His realpolitik approach, which prioritized national interest over ideological considerations, shaped his policies.
The détente policy with the Soviet Union was a hallmark of Kissinger’s strategy, focusing on easing tensions through diplomatic means. This approach led to significant arms control agreements, such as the Strategic Arms Limitation Talks (SALT I).
Even in the Middle East, Kissinger played a crucial role in diplomatic efforts, particularly with the 1973 Yom Kippur War and the subsequent peace agreements between Israel and its Arab neighbors. The Camp David Accords in 1978, brokered by Kissinger, marked a historic step toward stability in the region.
Henry Kissinger’s upbringing during the Nazi era significantly influenced his worldview and is speculated to have played a role in shaping his approach toward international affairs, including the Vietnam War. The experience of witnessing the atrocities committed by the Nazis and the impact of political upheaval on his own life likely left a lasting impression on Kissinger.
The trauma of his early years are speculated to have influenced Kissinger’s belief in the importance of maintaining a strong and assertive foreign policy. Living through a period marked by authoritarianism and persecution instilled in him a deep-seated desire to prevent similar threats to stability.
Critics argue that Kissinger’s policies were often driven by an approach that prioritized stability over human rights concerns. His role in the secret bombing of Cambodia during the Vietnam War and support for authoritarian regimes have been major subjects of controversy.
However, Kissinger’s experiences as a refugee and witnessing the consequences of unchecked power could have influenced his perception of global politics. This lens, shaped by the horrors of the Nazi era, might explain his commitment to interfering in Vietnam, even if it meant making controversial and morally ambiguous decisions in pursuit of perceived national interests.
His geopolitical calculations were influenced by the context of the Cold War, where the U.S. and the Soviet Union vied for global influence. His actions were often responses to complex international dynamics, seeking to maintain U.S. interests in a polarized world.
While some praise Kissinger for his diplomatic successes—especially in the Vietnam War—, others criticize the moral implications of his decisions. Understanding his actions requires consideration of the historical context and the complex geopolitical landscape of the time. When I asked students on campus if they knew who Kissinger was, many said no, so it is important as we look back on his lifelong efforts for American peace to share and acknowledge that his presence in politics will be missed.